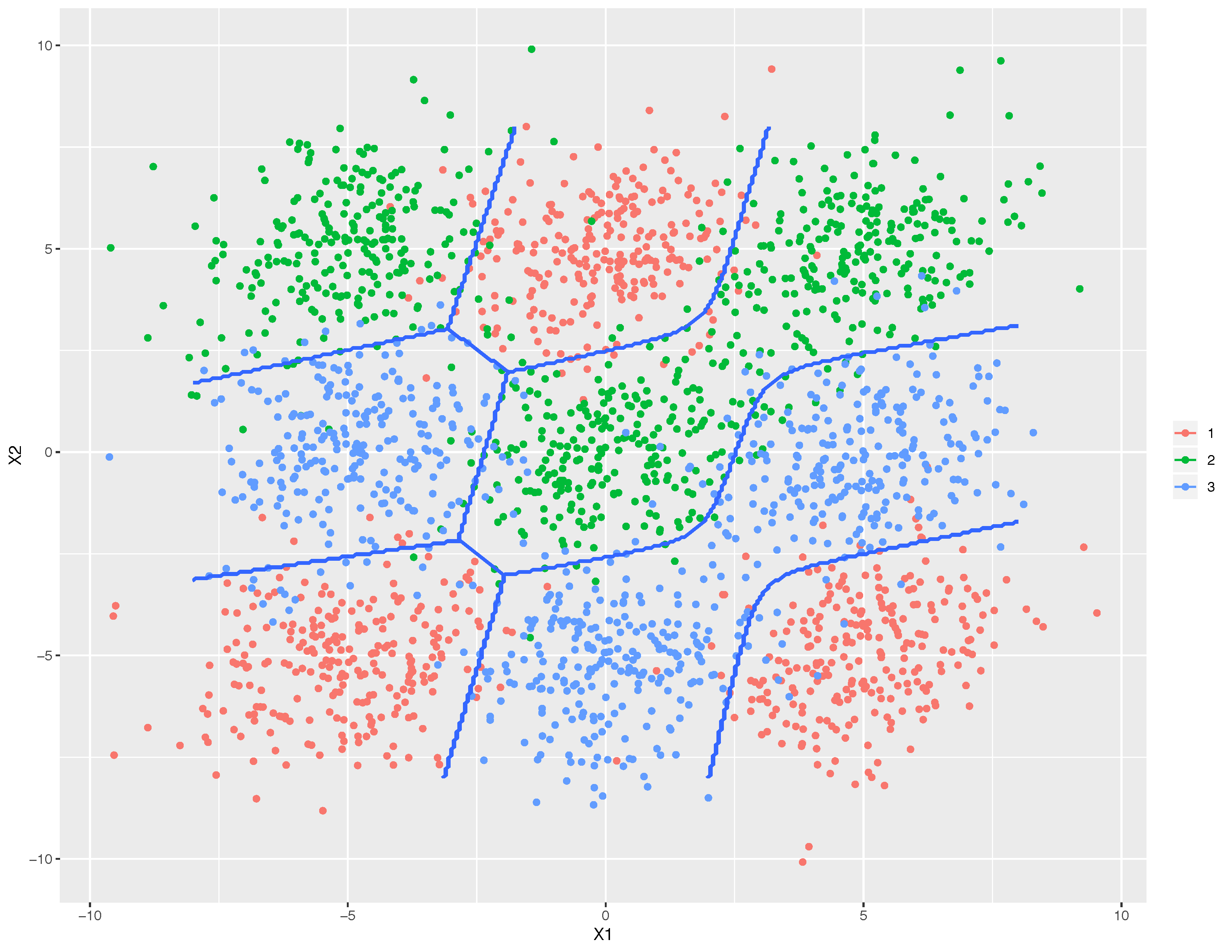
Discriminant analysis is a predictive modelling technique used to identify relationships between variables and the classifications of outcomes. It is often applied in cases where there is a need to differentiate among two or more groups of observations, for example in determining whether a customer will respond positively or negatively to a marketing campaign; or, predicting which group an individual belongs to based on their attributes and characteristics.
Discriminant Analysis For Classification and Prediction
Discriminant analysis can be used for both classification and prediction purposes. In classification tasks, it can help classify new observations into one of two (or more) possible types, like whether someone will buy a product or not. In prediction tasks, it can provide information about which factors are most important for predicting the outcome. For example, given data about customers and their purchases, discriminant analysis may reveal which demographic factors (e.g., age, gender) are most important for predicting customer loyalty or future purchases.
Working of Discriminant Analysis
The technique works by looking at differences in the mean values and covariance matrices of different groups of data points. Discriminant analysis looks at how different sets of independent variables (such as income level or gender) affect the dependent variable (such as purchase decisions). It then uses this information to draw conclusions about which independent variables are most important in predicting the dependent variable. Discriminant analysis can also quantify how likely each observation is to belong to a particular group by measuring how much its values deviate from the group’s mean value on each variable used in the analysis.
Applications of Discriminant Analysis
The best-fit line created through discriminant analysis allows researchers to accurately predict what type of group an observation falls into with greater accuracy than simply looking at single attribute values alone. In addition to its applications in marketing research and other fields that require data classification and prediction tasks, discriminant analysis has also been used in psychology research for test validity studies, such as studies that examine how well different tests measure certain traits or abilities across multiple populations. It can also be used to explore differences between populations on psychological traits like personality type or intelligence level – making it an invaluable tool for researchers who seek to understand behaviour better and improve educational practices accordingly.
Discriminant analysis is a statistical technique used to classify objects or cases into two or more groups based on a set of predictor variables. This method is commonly used in fields such as education, biology, and business to identify which variables contribute most to the differences between groups.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the main advantages of discriminant analysis is its ability to identify which variables are most important in distinguishing between groups. This allows researchers to identify the most relevant factors and to focus on these in further investigation. Further, discriminant analysis is a powerful tool for reducing the dimensionality of data. It can identify a small number of variables that are most important in distinguishing between groups, which is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets.
However, discriminant analysis also has some disadvantages. One limitation is that it assumes that the variables used to predict group membership are normally distributed. This assumption cannot always be met in practice, and violations of this assumption can result in inaccurate classification results. Another limitation is that discriminant analysis assumes that the predictor variables have equal covariance matrices across groups. This assumption can also be violated in practice, which can lead to biased classification results.
Conclusion
Overall, discriminant analysis is a useful statistical technique that can provide valuable insights into group differences. However, researchers should be aware of its limitations and the assumptions that underlie its use.