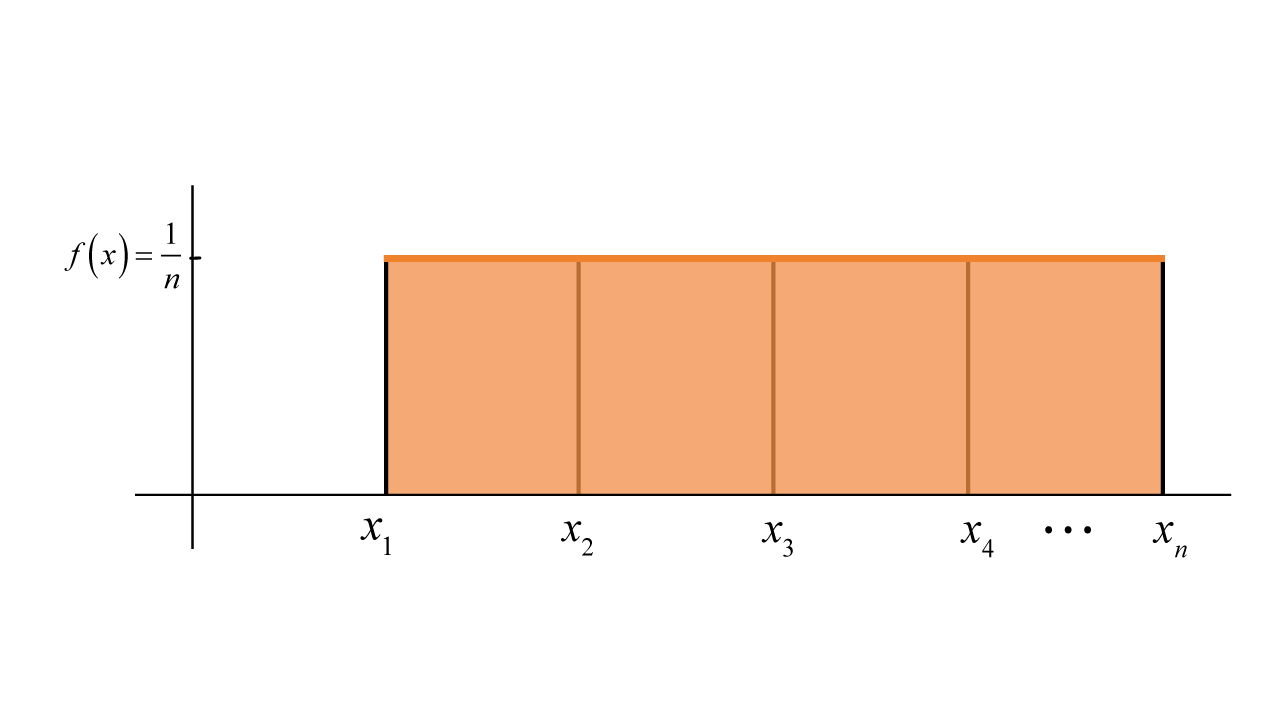
Discrete uniform distribution is a type of probability distribution in which all k distinct values have the same probability of occurring. A discrete uniform distribution is often represented by a set of 𝑥1, 𝑥2, 𝑥3,… , 𝑥𝑘 with equal probabilities for each value. The maximum value in this range is known as the maximum value or upper limit and the minimum value is known as the minimum value or lower limit. This range can be any size and may not always start from zero. The probability associated with each x-value in this range is 1/k where k represents the total number of elements in the set. This means that if there are k values, each value will occur with probability of 1/k.
Uses of Discrete Uniform Distribution
This type of distribution is often used to model the number of successes in a given number of trials for events with equally likely outcomes. One example could be a coin flip: if a coin is flipped two times, then the probability of both flips being heads is equal to 1/4. This is because the two possible outcomes (heads or tails) each have an equal chance (1/2) of occurring and since there are two flips, the total probability would be 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4. All other possible combinations (two heads, one head and one tail, no heads etc.) would also have an equal chance of occurrence.
The discrete uniform distribution can also be used to represent a random variable’s behavior over time or space. For example, if we were to roll a six-sided die multiple times, we would expect that each individual side would have an equal chance (1 in 6) of being rolled each time and that overall all sides would appear around the same amount during our experiment (assuming enough rolls). The discrete uniform distribution is most often seen when dealing with finite samples or data points such as flipping coins, rolling dice and doing surveys which ask questions with finite answers such as yes/no or agree/disagree. It can also be used to represent continuous variables such as temperatures over time or distances between points on a map.
This type of distribution has many useful applications in statistical analysis such as hypothesis testing and estimation techniques like maximum likelihood estimation. In addition to this, it can also help us better understand different types of data distributions by providing us with information about their shape and spread which can give us additional insights into how certain variables interact with each other. Discrete uniform distribution refers to a probability distribution where all possible outcomes are equally likely.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of its main advantages is its simplicity. It is easy to understand and apply, which makes it a popular choice when modeling situations with a finite number of outcomes. Additionally, it can be used as a baseline for more complex models, providing a basis for comparison and evaluation. However, one of the major disadvantages of discrete uniform distribution is its restrictive nature. It assumes that all possible outcomes are equally likely, which is not necessarily the case in real-life situations. Furthermore, it can be limiting in cases where there are too many possible outcomes, as the probability of each outcome becomes increasingly smaller. Another limitation of the discrete uniform distribution is that it assumes the outcomes are all discrete and independent. In many cases, this assumption may not hold, and a more complex model may be required to accurately capture the relationship between outcomes.
Conclusion
Despite these limitations, the discrete uniform distribution is a valuable tool for statisticians and data scientists. Its simplicity and versatility make it a useful starting point for modeling many real-world situations, and it can provide valuable insights even in cases where a more complex model is required.