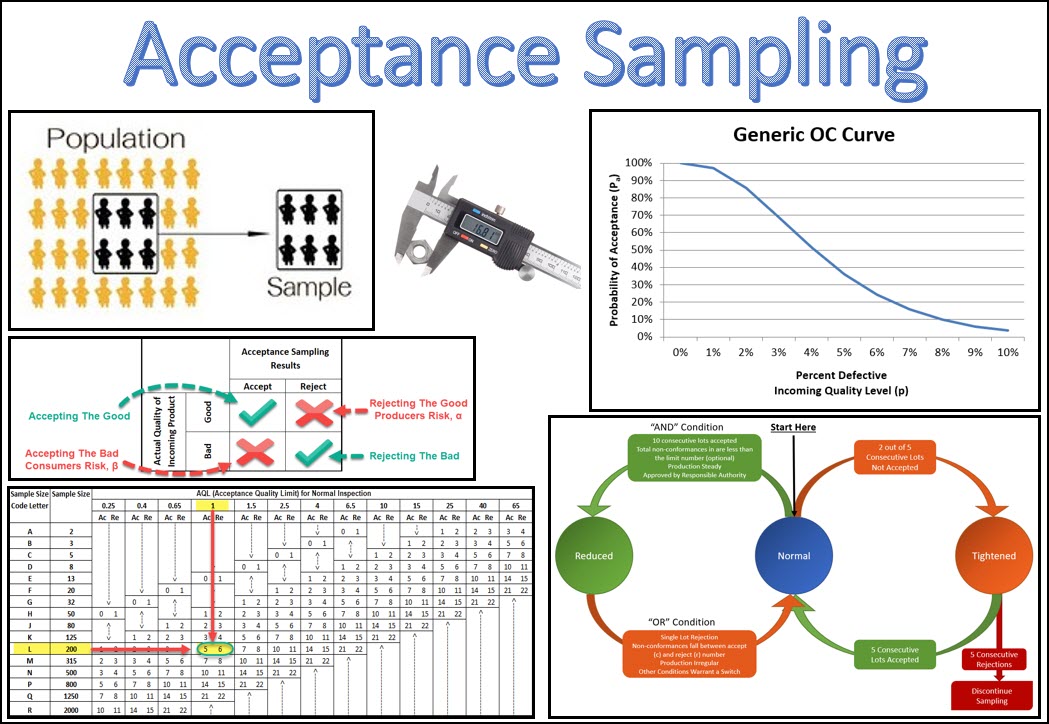
Acceptance sampling is a statistical method used in quality control. It involves inspecting a random sample of products or services from a larger batch to determine if the entire batch meets the specified quality standards. This method is commonly used in manufacturing processes where it is impractical or too expensive to inspect all units in a batch. The sample size and the acceptance criteria are determined by the producer and the consumer based on the level of risk they are willing to accept. Acceptance sampling is a valuable tool when used correctly, as it is cost-effective and allows for quick decisions on whether to accept or reject a batch.
Types of Acceptance Sampling
There are two main types of acceptance sampling: attribute sampling and variable sampling. Attribute sampling is used when the quality characteristic being inspected is categorical. For example, inspecting a batch of t-shirts for defects such as rips, stains or wrong sizing. Variable sampling is used when the quality characteristic being inspected is continuous. For example, measuring the weight or length of a batch of wires. When performing acceptance sampling, it is important to ensure that the sample is truly random and representative of the entire batch. Failure to do so may result in incorrect decisions and waste valuable resources. In addition, it is important to periodically review and update the acceptance criteria to reflect changes in the product or service being inspected.
Various Definitions
Acceptance Sampling is a type of quality control procedure in which a sample is taken from a collection or batch of items, and the decision to accept the batch as satisfactory, or reject them as unsatisfactory, is based on the proportion of defective items in the sample. That is, a sample of the items from a batch is drawn and tested for its quality, and the results are considered representative of the entire batch.
Acceptance sampling can be defined as a statistical measure, which is used as a quality control statistic. It allows the researcher to find the quality of a batch of goods, by selecting a particular number of items for the purpose of testing. The quality assessed for the selected group of items will be viewed and considered representative of the entire product range. That is, acceptance sampling is a form of representative sampling and testing for ascertaining the defects in the products.
Steps in Acceptance Sampling
Under the process of acceptance sampling, the first step is to determine the batch size that needs to be tested, and the number of products that need to be included in the batch for sampling. The acceptable number of defects within the sample batch is also determined. In the next step, products are selected randomly, before they are to be shipped. The statistical reliability of the sample is tested with the help of t-statistic, which is defined as an inferential statistic and used for determining whether there is a significant difference between two different groups, sharing homogenous characteristics. The main aim of acceptance sampling is to find out the quality of the entire batch, without having to test each and every unit. Based on the results of the batch, it is decided whether the batch is accepted or rejected. That is if the number of defects in the batch exceeds the acceptance number of defects, the entire batch will be rejected, and vice-versa.
Conclusion
In conclusion, acceptance sampling is a widely used statistical method in quality control. It is a cost-effective and efficient way of determining the quality of a batch of products or services. However, careful planning and execution are needed to ensure the method is reliable and accurate.