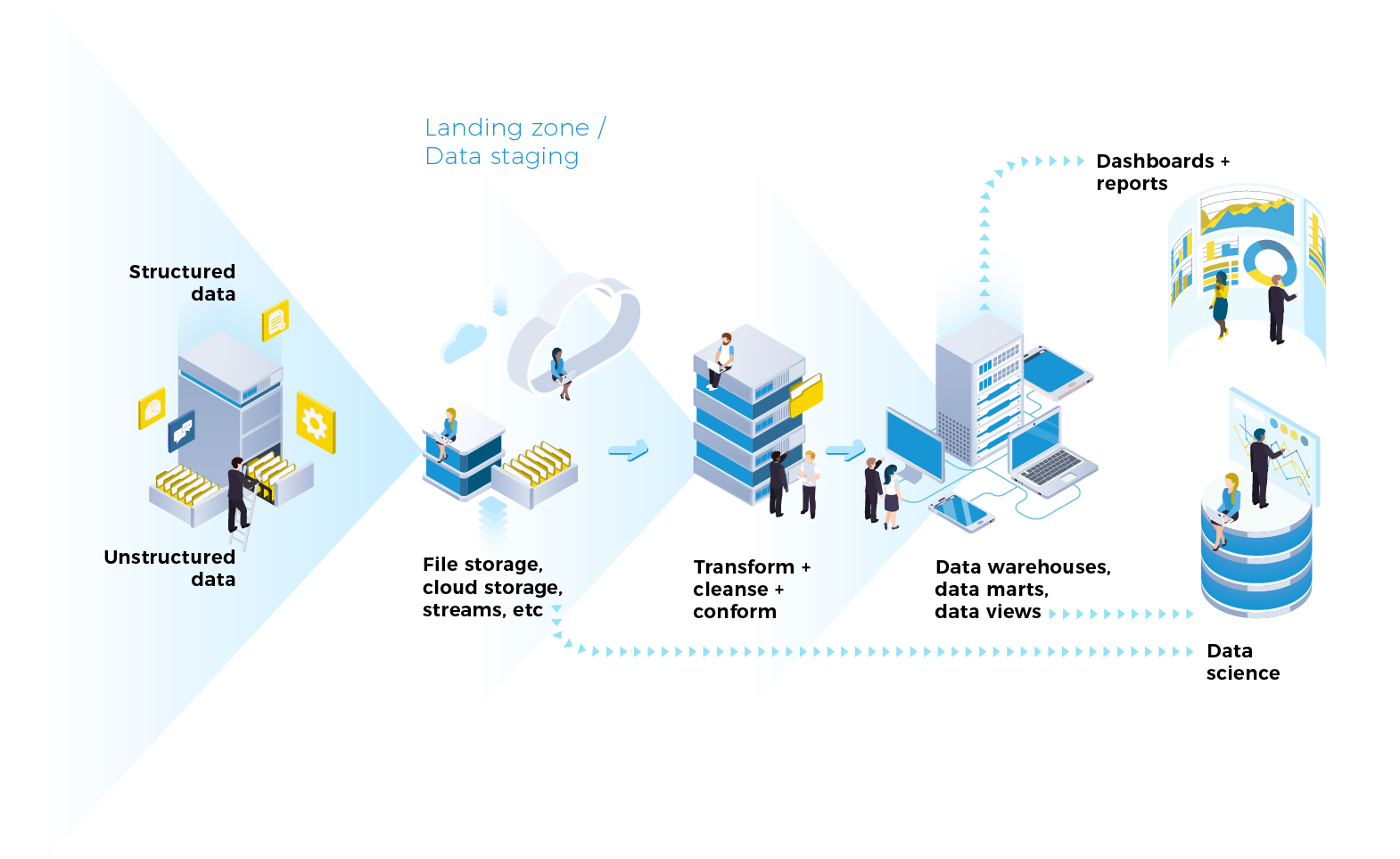
A data pipeline is a set of processes that allow for the efficient and reliable flow of information from one computing system to another. It enables organizations to move large volumes of data between different sources in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Uses of Data Pipelines
Data pipelines also enable organizations to collect, cleanse, transform and store data in order to better utilize it for various tasks such as reporting, analytics or machine learning. Data pipelines can help streamline data collection processes by providing access to clean, structured data from multiple sources.
They provide an automated process for collecting, transforming, validating and delivering high-quality data into target applications while reducing manual effort and cost of development.
Data pipelines can also be used to automate the deployment of applications into production environments without manual intervention. In addition, data pipelines often require less human involvement than manual processes due to its automation capabilities.
This helps reduce potential errors as well as accelerating time-to-value. Moreover, they provide higher levels of flexibility which allows users to quickly adjust their processes with minimal disruption.
Technologies Used in Data Pipelines
Data Pipelines use various technologies such as Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) tools, streaming systems like Apache Kafka, cloud services like Amazon Kinesis or Azure Stream Analytics, Hadoop clusters and more. All these technologies are used together to create reliable pipelines that can handle vast amounts of data with greater accuracy than manual processes. The components of a Data Pipeline typically include:
- Sources: where the raw data resides;
- Connectors: which move the data from one source to another;
- Transformation functions: which convert the raw incoming data into formats required by applications;
- Destination platform: where the structured output is stored;
- Quality checks or monitoring agents: which ensure correctness of results;
- Security protocols: which protect against unauthorized access;
- Scheduler: which sets conditions under which transformations will run; and
Data Virtualization layers: which provide visibility into underlying datasets without having to copy them all over again. Data pipelines are often used in conjunction with other technologies such as real-time streaming architecture or batch processing systems in order to provide improved performance.
Data pipelines are increasingly being used in various industries including retail, manufacturing and healthcare due to their ability to streamline data management and ensure accuracy at scale.
As businesses become more reliant on these technologies for decision-making, the importance of having reliable and secure data pipelines will continue to grow exponentially. However, data pipelines also have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, which must be considered before their implementation.
Advantages
- Increased Efficiency: Data pipelines automate data transfer between systems, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This reduces the number of errors and time-consuming tasks, resulting in increased efficiency and overall cost savings.
- Data Accuracy: Data pipelines ensure data consistency and accuracy by performing data validation, cleansing, and transformation tasks. This helps to eliminate human errors and inconsistencies, resulting in high-quality data that can be trusted for analysis and decision-making.
- Scalability: Data pipelines can handle large volumes of data, making them ideal for organizations with high data processing needs. They can also be easily scaled up or down based on changing business needs.
- Accessibility: Data pipelines create a centralized data repository that is easily accessible to authorized users. This makes it easier for different departments and users to access data for analysis and decision-making.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Developing and maintaining data pipelines can be complex, requiring a high level of technical expertise. Organizations need to invest significant time and resources in creating and managing pipelines.
- Cost: Data pipelines can be expensive to implement and maintain, especially for organizations with complex data processing needs. This can be a barrier for smaller organizations, which may not have the resources to implement data pipelines.
- Security Risks: Data pipelines can pose security risks if they are not designed and implemented correctly. Organizations need to ensure that their pipelines are secure and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Maintenance: Data pipelines require regular maintenance and updates to ensure that they continue to function correctly. This can be time-consuming and may require organizations to invest in additional resources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data pipelines offer many advantages, including increased efficiency, data accuracy, scalability, and accessibility. However, they also have their own set of challenges, including complexity, cost, security risks, and maintenance requirements. Organizations need to carefully consider these advantages and disadvantages before implementing data pipelines to ensure that they are the right choice for their business needs.