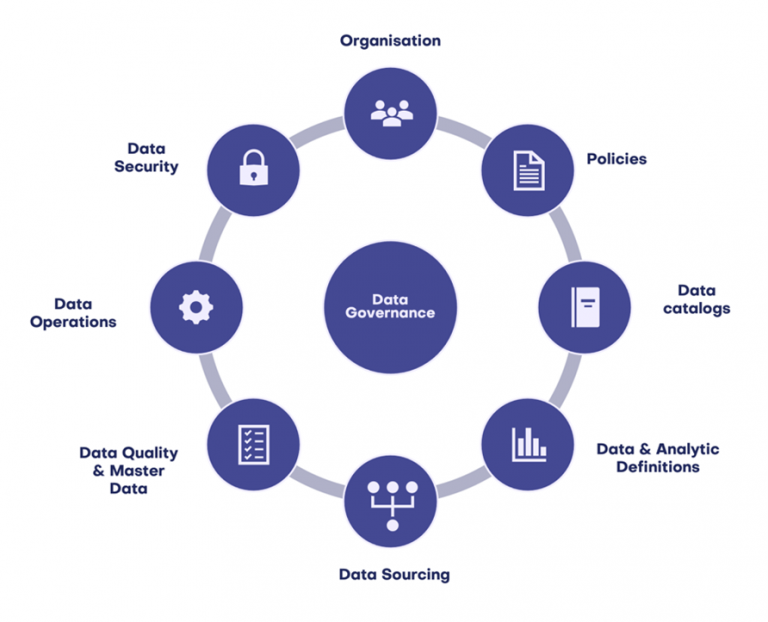
Data Governance- Planning is the process of creating a plan for data governance, which is the process of managing and securing data and information within an organization. It includes defining policies, procedures and controls that ensure the accuracy, quality, consistency, security, and integrity of data throughout its lifecycle.
Comprehensive Approach
Also Data Governance is a comprehensive approach to managing data across an organization. It allows businesses to control and monitor the quality, accessibility, security, and ownership of all data.
Uses of Data Governance
Data Governance seeks to ensure that data is used effectively and efficiently throughout the enterprise. It also helps protect against misuse or abuse of data, as well as ensuring compliance with any laws or regulations related to the handling of confidential or sensitive information.
This includes defining roles and responsibilities for ensuring that these policies are carried out properly. Planning for Data Governance also requires assessing existing systems and processes to identify gaps in data management practices; this can be done through interviews with users or surveys about their experience with different systems. Organizations may need to develop new tools or use existing tools such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to help manage data more effectively.
Additionally, organizations need to put into place clear IT architectures that define how data flows across different departments or applications, as well as access policies that govern who has access to what information.
Training may also be necessary so that personnel understand how they should handle sensitive information and comply with laws and regulations. Finally, it’s important to create processes for regularly auditing the system’s effectiveness and making sure it is updated if any changes occur in terms of technology or regulations.
These audits should document any issues or potential risks related to data governance in order to reduce potential damages from non-compliance or breaches of security protocols. Additionally, organizations should ensure that all personnel are trained on proper procedures and have access to resources such as quick reference guides during their work day so that successful implementation of data governance-planning can be achieved.
It is a crucial facet of businesses and organizations, and it comes with both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Better Data Quality: Data Governance ensures that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and up-to-date. This leads to better decision-making, improved operational efficiencies, and higher customer satisfaction.
- Compliance: Data Governance helps businesses and organizations comply with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies. It reduces legal risks and avoids penalties and fines.
- Data Protection: Data Governance ensures that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access, theft, or loss. This safeguards the reputation and trust of businesses and organizations.
- Collaboration: Data Governance encourages collaboration between different departments and teams. This creates a culture of data sharing, enhances communication, and fosters innovation.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Data Governance can be expensive, depending on the size, complexity, and scope of the organization. It requires investment in technology, tools, infrastructure, and personnel.
- Time: Data Governance takes time to implement and maintain. It requires significant effort, planning, and coordination to ensure that the policies and processes are effective and efficient.
- Resistance: Data Governance can face resistance from employees who are reluctant to change their habits or follow new rules. This can lead to low adoption rates, poor compliance, and increased risks.
- Complexity: Data Governance can be complex and difficult to understand for non-experts. It requires specialized expertise and knowledge, such as data management, security, and compliance.
Process of Data Governance
Data Governance- Planning is the process of creating a plan for data governance, which is the process of managing and securing data and information within an organization. It includes defining policies, procedures and controls that ensure the accuracy, quality, consistency, security, and integrity of data throughout its lifecycle.
Also Data Governance is a comprehensive approach to managing data across an organization. It allows businesses to control and monitor the quality, accessibility, security, and ownership of all data.
Data Governance seeks to ensure that data is used effectively and efficiently throughout the enterprise. It also helps protect against misuse or abuse of data, as well as ensuring compliance with any laws or regulations related to the handling of confidential or sensitive information.
Roles and Responsibilities of Data Governance
This includes defining roles and responsibilities for ensuring that these policies are carried out properly. Planning for Data Governance also requires assessing existing systems and processes to identify gaps in data management practices; this can be done through interviews with users or surveys about their experience with different systems. Organizations may need to develop new tools or use existing tools such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to help manage data more effectively.
Additionally, organizations need to put into place clear IT architectures that define how data flows across different departments or applications, as well as access policies that govern who has access to what information. Training may also be necessary so that personnel understand how they should handle sensitive information and comply with laws and regulations.
Finally, it’s important to create processes for regularly auditing the system’s effectiveness and making sure it is updated if any changes occur in terms of technology or regulations. These audits should document any issues or potential risks related to data governance in order to reduce potential damages from non-compliance or breaches of security protocols. Additionally, organizations should ensure that all personnel are trained on proper procedures and have access to resources such as quick reference guides during their work day so that successful implementation of data governance-planning can be achieved.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Data Governance has both advantages and disadvantages. While it can improve the quality, compliance, protection, and collaboration of data, it can also be costly, time-consuming, and face resistance and complexity. Therefore, businesses and organizations should carefully evaluate their needs, goals, and resources before implementing Data Governance.