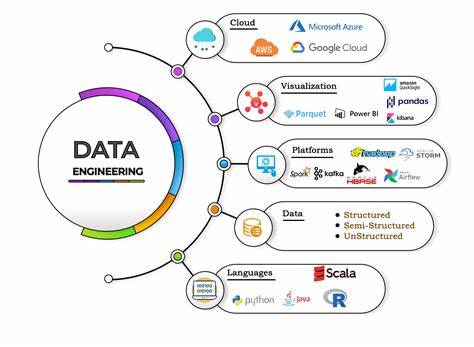
Data engineering (DE) is an important part of any data analysis and analytics strategy, as it enables the effective storage and retrieval of large volumes of data. Scaling data access involves a variety of techniques to ensure that the right data is available when needed, which can include sharding, indexing, partitioning, caching, and replication.
Important Role
Data engineering (DE) is an important part of any data analysis and analytics strategy, as it enables the effective storage and retrieval of large volumes of data. Scaling data access involves a variety of techniques to ensure that the right data is available when needed, which can include sharing, indexing, partitioning, caching, and replication.
Data Engineering (DE) involves the acquisition, storage and organization of data in order to make it accessible and useful. DE professionals design and build systems that enable organizations to store large volumes of data and process it quickly.
Techniques In Data Engineering
By applying techniques such as sharding, indexing, partitioning, caching and replication, they can ensure that the right data is available when needed. DE engineers work on gathering data from various sources including databases, web services, sensors and other digital sources. They also perform activities such as cleansing and transforming this data into an optimized format for effective storage.
Furthermore, they are responsible for creating efficient structures for storing and analyzing different types of data using technologies such as Hadoop, Apache Spark or Apache Cassandra. Using these tools helps create a distributed computing environment which allows for quick access to data from multiple sources even during peak times of usage.
In addition to managing the physical infrastructure of data storage systems, DE professionals also need to be aware of the security implications involved in handling sensitive information. To this end, they must have an understanding of encryption algorithms and cryptography principles in order to ensure that all confidential data remains secure while being transferred or processed.
Analytical Projects
In addition to this they must also set rules governing how users interact with the system as well as setting up access control policies based on user permissions and roles. Data engineering plays a critical role in modern analytics projects due to its ability to process huge amounts of structured and unstructured data quickly.
The integration of traditional business intelligence tools with advanced analytical technologies such as machine learning enables organizations to gain valuable insights from their stored information which can lead to greater success in their operations.
By relying on experienced DE professionals who possess strong problem-solving skills along with technical knowledge and expertise related to big data technology organizations can ensure their overall success through successful management of their enterprise’s digital assets.
While there are a number of advantages to being a data engineer, there are also some disadvantages that must be weighed and considered. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of being a data engineer.
Advantages
- High Demand – The demand for data engineers continues to grow each year, with data being more important than ever before. As a result, job opportunities are plentiful and well-compensated.
- Job Satisfaction – Creating data solutions and optimizing data pipelines can be incredibly fulfilling, as data engineers get to see the results of their work in real-time.
- Opportunities for Growth – Data engineering requires a diverse skill set and continuous learning as technology evolves. This means that there is always the opportunity for data engineers to expand their knowledge and career prospects.
- Variety of Industries – Data engineering spans across a broad range of industries, meaning that data engineers can pursue careers in sectors from finance to healthcare to software development.
Disadvantages
- Intensive Workload – Data engineering can often involve long hours, tight deadlines, and a significant workload. The process of cleaning, structuring, and organizing data can be quite laborious and time-consuming.
- Technical Complexity – Data engineering requires a certain level of technical expertise and experience, meaning that it can be difficult for newcomers to break into the field.
- Continuous Learning – As technology continues to evolve, data engineers must continuously learn new skills and techniques to remain competitive.
- Data Security – With the increasing importance and prevalence of data, data security is a pressing concern. Data engineers must be vigilant about maintaining the security of sensitive information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data engineering is a highly valuable and rewarding profession that offers many opportunities for growth and job satisfaction. However, it is not without its challenges, such as a high workload and technical complexity. Nevertheless, for those with the right skills and mindset, data engineering can be an outstanding career path with opportunities for growth and innovation.